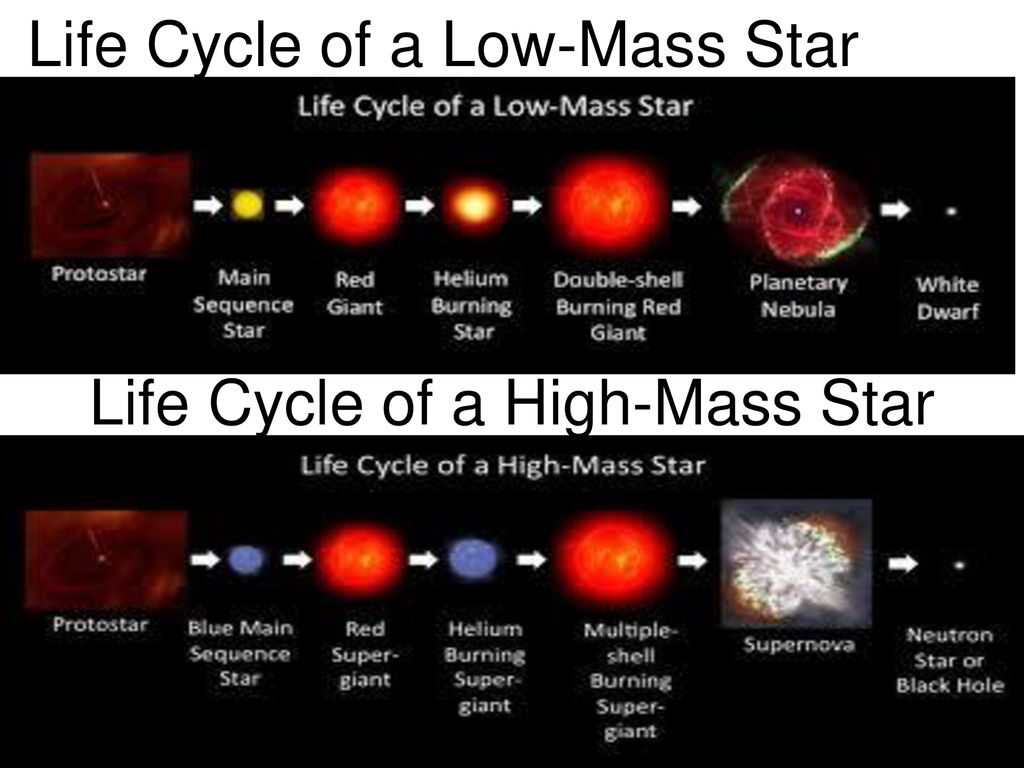
Describe the Life Cycle of a High Mass Star
Describe the 3 types of galaxies -- at least one characteristic of each. Throughout their lives stars fight the inward pull of the force of gravity.
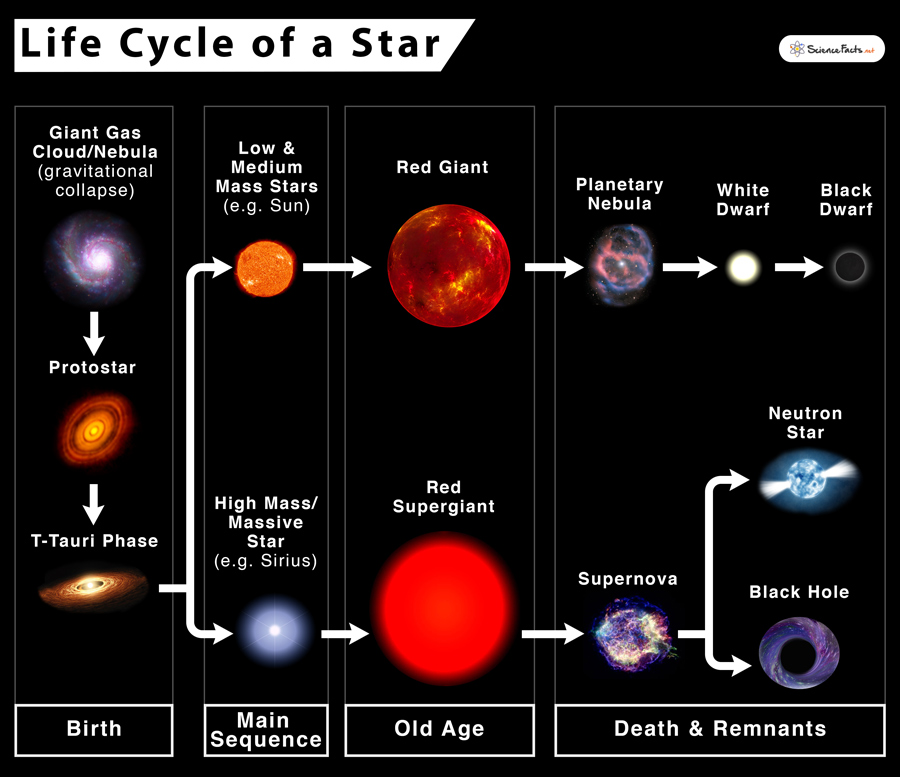
Life Cycle Of A Star Stages Facts And Diagrams
The life cycle of a star larger than the Sun starts in the same way as a solar mass star.
. When this reaches 15000000C nuclear fusion begins and causes to form a new star or protostar. A larger mass star will colapse and turn into a black hole. It is only the outward pressure created by the nuclear reactions pushing away from the stars core that keeps the star intact.
Step 4 - Red - The star expands into a red giant when the stars hydrogen level drops. Eventually the supply of hydrogen runs out and the star begins its demise. A high mass Star after burning hydrogen to Helium Helium to Carbon will also burn Carbon into other heavier elements like Neon Magnesium Oxygen and some can even go all the way up to Iron where the Nuclear Fusion eventually Stops.
Many elements fuse in shells. The force of gravity within a nebula pulls the particles closer together until it. View the full answer.
The core remains as a white dwarf and eventually cools to become a black dwarf. A massive star will undergo a supernova explosion. In the core of a high mass star four hydrogen nuclei form into a single helium nucleus by the series of reactions known as the CNO carbon-nitrogen-oxygen cycle.
Once a protostar forms its life cycle is fixed. The Life Cycle of a High-Mass Star Sciencing A stars life cycle is determined by its mass--the larger its mass the shorter its life. Sciencing_Icons_Science SCIENCE Sciencing_Icons_Biology Biology Sciencing_Icons_Cells Cells Sciencing_Icons_Molecular Molecular.
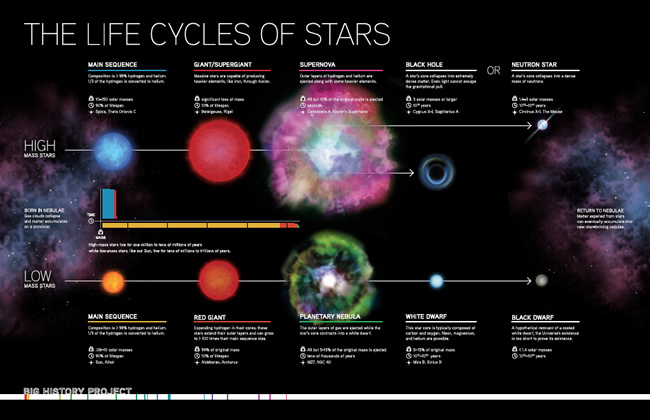
H fuses to He in shell around He core. If the remnant of the explosion is 14 to about 3 times as massive as our Sun it will become a neutron star. Supernova leaves neutron star behind.
But these nuclear reactions require fuel in particular hydrogen. That is what would happen to a star with a low mass like our sun also the life time of a star depends on its mass. The life cycle of a star larger than the Sun starts in the same way as a solar mass star.
Discuss briefly why the Greenhouse Effect could be a problem and an asset for humans and all life on the planet. The main sequence star may live millions or even billions of years. Answer in 4 sentences or more.
What are the main. At the end of a high-mass stars fusion process iron composes the stars core. The hydrogen in the core burns until only helium is left.
Life Stages of High-Mass Star 1. All stars form from a giant cloud of hydrogen gas and dust called a nebula. Step 6 - White - Fusion stops and a supernova explosion occurs.
H fuses to He in core. Hydrogen atoms forms a spinning cloud of gas and eventually pulls more hydrogen gas to the spinning cloud. High-mass stars have lives of 10 million years versus 10 to 50 billion years or more for low-mass stars.
Like low-mass stars high-mass stars are born in nebulae and evolve and live in the Main Sequence. The pressure at the stars iron-laden core continues to build until the ultimate cosmic. For HIGH mass stars- 1.
Most of the star is blown away. This is mostly done through interacting with the students as they work in groups and present information at the end of the class. All stars form from a giant cloud of hydrogen gas and dust called a nebula.
The force of gravity within a nebula pulls the particles closer together until it. He fuses to C in core while H fuses to He in shell. Describe the life cycle of stars--high mass star medium mass star and a low mass star.
For example the Milky Way is forming stars at a rate of a few M per year such that massive stars die at a rate of approximately one per century. Then the core contracts while the outer layers expand. Answer all questions for upvote 1Describe the life cycle of stars--high mass star medium mass star and a low mass star.
Massive stars transform into supernovae neutron stars and black holes while average stars like the sun end life as a white dwarf surrounded by a disappearing planetary nebula. You could ask them to write up the life cycle of a star for the high and low mass cases and turn that in. Associated files and images.
No nuclear fusion of iron is possible out of a high-mass star core which has the same mass as our entire Sun. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. LMlow mass HMhigh mass LM1 molecular cloud LM2 main sequence star LM3 H shell burn He.
Expert Answer 100 1 rating stars life cycle is determined by its mass. Start studying Life cycle of a high mass star. All stars irrespective of their size follow the same 7 stage cycle they start as a.
Step 5 - Orange - Different fusion processes occur. A larger star with more mass will go on making nuclear reactions getting hotter and expanding until it explodes as a supernova. Advertisement New questions in Physics.
The larger its mass the shorter its life cycleany stars are formed in clouds of gas and dust k. The lifetimes of massive stars are short up to a few tens of million years see figure 1 because of their high luminosities so their death rate closely mimics the stellar birth rate. High-mass stars usually have five stages in their life cycles.
How does the life cycle of a high mass star start. As it spins hydrogen atoms start to collide with each other and hydrogen gas heats up. The star expands cools and loses mass each time.

Life Of A High Mass Star Diagram Quizlet
Mr Toogood Physics Life Cycle Of Stars Supernovae Black Holes And Neutron Stars
No comments for "Describe the Life Cycle of a High Mass Star"
Post a Comment